Arrythmias and Heart Rhythm (AF)
What information does BP+ give on arrhythmias?
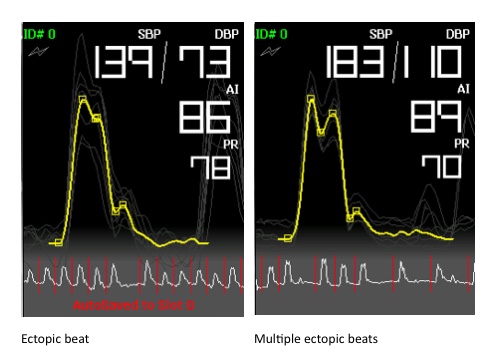
BP+ provides a rhythm strip over 10 seconds with each pulse being clearly identifiable. BP+ also calculates a numerical measure of short term pulse rate variability. Two examples of arrhythmias as presented by a cardiovascular monitor are shown blow:
Diagnosis of Atrial Fibrillation Using the Pulsecor Cardioscope Blood Pressure Device
Background: Atrial fibrillation (Afib) may first be diagnosed only after presentation with heart failure or stroke. Identification of Afib by non-medical staff when measuring blood pressure (BP) may improve its’ detection in asymptomatic patients in primary care. The Pulsecor CardioScope is a user friendly automated sphygmomanometer previously validated for estimating central BP. Analysis of beat-to-beat variation in the pulse wave amplitude or RR interval could also be used to diagnose Afib.
Methods: Patients presented for pre-clinic BP measurement and electrocardiogram (ECG) were recruited. ECG technicians performed BP measurement using Pulsecor and an ECG simultaneously. Pulse wave parameters calculated by Pulsecor were tested for performance in correctly classifying rhythm as Afib and Sinus via pulse rate variability (PRV) using √mean [(period 2 − period 1)2], pulse amplitude variation (PAV) using [max(pulse amplitude) − min(pulse amplitude)]/mean(pulse amplitude) and signal to noise ratio (SNR). Pulsecor analysis was performed blind to ECG results. Diagnoses of arrhythmias were confirmed by Cardiology Registrars interpreting corresponding ECGs.
Results: Forty-five patients (mean age 70 ± 12 years; 71% men) with Afib on ECG, and 55 patients (mean age 60 ± 17 years; 44% men) with normal sinus rhythm. 100% sensitivity to Afib was associated with a 13% false positive rate; 96% sensitivity with 7% false positive rate when using PRV for rhythm classification. PRV demonstrated the highest accuracy [Area under the curve (AUC) = 0.953] to detect Afib when comparing with PAV (AUC = 0.844) and SNR (AUC = 0.857).
Conclusions: Pulsecor device can diagnose Afib with high sensitivity, and can be used to screen for Afib with BP measurement in primary care.
Pulse Wave Variability Detects Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
Pulse rate variability predicts atrial fibrillation and cerebrovascular events in a large, population-based cohort (SLUYTER, J. D et al., 2019).
Elevated RMSSD (>100ms) or IrrIx (>7.7%) values indicative of the presence of AF predict future AF and cerebrovascular events; more so with increasing pulse irregularity and even among those without prior AF diagnosis.
Diagnosis of Atrial Fibrillation Using the Pulsecor Cardioscope Blood Pressure Device (BP+) (T.Oh et al., 2013).